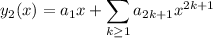Assume a general solution of the form
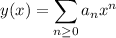
with derivatives
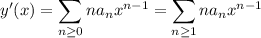
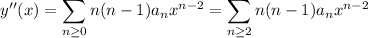
Substituting into the ODE gives

The first sum starts with degree 0; the second starts with degree 1; and the third starts with degree 0. So remove the first term from the first and third sums, then consolidate everything into one sum by shifting indices as needed.
First sum:
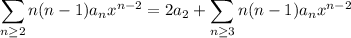
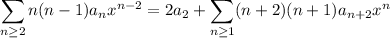
Third sum:
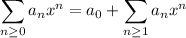
So the ODE can be expressed as
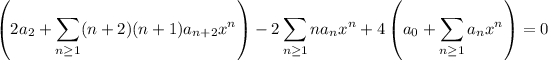

Then the coefficients are given by the recurrence,
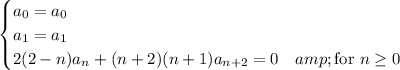
Notice that we should have
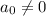 and
and
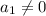 in order to get non-zero solutions.
in order to get non-zero solutions.
For
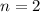 , we would find that
, we would find that
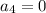 , which would imply that
, which would imply that
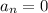 for all even
for all even
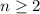 . Then the even-indexed terms in the series contribute one solution,
. Then the even-indexed terms in the series contribute one solution,
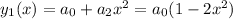 .
.
On the other hand, for odd
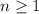 we have
we have
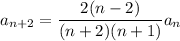
With
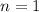 :
:
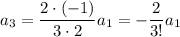
With
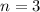 :
:
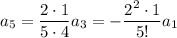
With
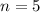 :
:

So the general pattern for
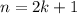 ,
,
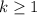 , is
, is
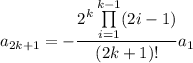
and we get a second (linearly independent) solution