Start with
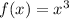
First transformation:
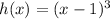
Type of transformation:
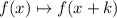
Effect: Every time you add a constant to the function argument, you translate its graph horizontally, k units to the left if k is positive, k units to the right if k is negative.
Second transformation:
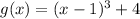
Type of transformation:
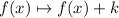
Effect: Every time you add a constant to the function, you translate its graph vertically, k units upwards if k is positive, k units downward if k is negative.
So, starting from the parent function, you translate its graph 1 unit right and 4 units up, and you have the graph of g(x).