Answer: The total pressure of a mixture is 1.247 atm.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the total pressure of the mixture of the gases, we use the equation given by Raoult's law, which is:
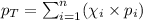
where,
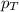 = total pressure of the mixture
= total pressure of the mixture
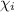 = mole fraction of i-th species
= mole fraction of i-th species
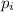 = partial pressure of i-th species
= partial pressure of i-th species
We are given:
Mole fraction of nitrogen = 0.5
Partial pressure of nitrogen = 1.7 atm
Mole fraction of oxygen = 0.23
Partial pressure of oxygen = 1.1 atm
Mole fraction of argon = 0.12
Partial pressure of argon = 0.7 atm
Mole fraction of methane = 0.10
Partial pressure of methane = 0.5 atm
Mole fraction of water vapor = 0.05
Partial pressure of water vapor = 0.2 atm
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![p_T=[(0.5* 1.7)+(0.23* 1.1)+(0.12* 0.7)+(0.10* 0.5)+(0.05* 0.2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/bwc375xjvpj47qv2q3avw5dmeswuf884qw.png)
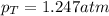
Hence, the total pressure of a mixture is 1.247 atm.