Answer : The 'q' for this reaction is, 328 J
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the moles of
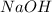 and
and
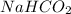 .
.
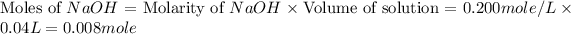
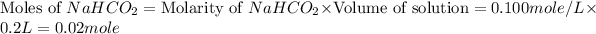
From this we conclude that, the moles of
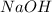 are less than moles of
are less than moles of
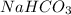 . So, the limiting reactant is, NaOH.
. So, the limiting reactant is, NaOH.
Now we have to calculate the 'q' for this reaction.
The balanced chemical reaction will be,
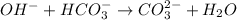
The expression used for 'q' of this reaction is:
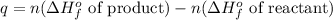
![q=n[(\Delta H_f^o\text{ of }CO_3^(2-))+(\Delta H_f^o\text{ of }H_2O)]-n[(\Delta H_f^o\text{ of }HCO_3^-)+(\Delta H_f^o\text{ of }OH^-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/187l3y8wnbhd9z3ln24s56gkznliysksg0.png)
where,
n = number of moles of limiting reactant = 0.008 mole
At room temperature,
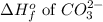 = -677 kJ/mole
= -677 kJ/mole
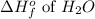 = -286 kJ/mole
= -286 kJ/mole
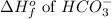 = -692 kJ/mole
= -692 kJ/mole
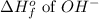 = -230 kJ/mole
= -230 kJ/mole
Now put all the given values in the above expression, we get:
![q=0.008mole[(-677kJ/mole)+(-286kJ/mole)]-0.008mole[(-692kJ/mole)+(-230kJ/mole)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/f4qeygccyaqcrkgn356ipm67hvify31hvj.png)
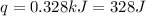 (conversion used : 1 kJ = 1000 J)
(conversion used : 1 kJ = 1000 J)
Therefore, the 'q' for this reaction is, 328 J