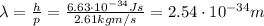Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, we need to find the final velocity of the ball just before it reaches the ground. Since the ball is in free-fall motion, its final velocity is given by
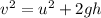
where
v is the final velocity
u = 0 is the initial velocity
g = 9.8 m/s^2 is the acceleration due to gravity
h = 39.8 m is the height of the building
Solving for v,
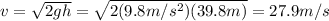
Now we can calculate the ball's momentum:
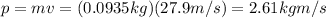
And now we can calculate the De Broglie's wavelength of the ball: