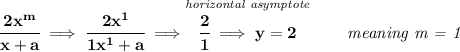for a rational expression the vertical asymptotes occur when the denominator equals 0, in this case that will be when x + a = 0.
now, if there were to be a vertical asymptote of x = 1, that simply means that
x = 1 ==> x - 1 = 0.
meaning that a = -1.
horizontal asymptotes occur when the denominator has a higher degree than the numerator OR when both have the same degree.
when the degree of the denominator is higher, then the only horizontal asymptote occurring is y = 0.
when the degrees are the same, then the horizontal asymptote occurs at the leading terms' coefficient fraction.
now, if this expression were to have a horizontal asymptote of y = 2, that simply means