Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Parameter given:
Volume of gas in the container = 22.4L
Pressure on the gas = 1.0atm
Temperature of the gas = 0.0°C
Problem 1
Coverting 0.0°C to Kelvin:
In order to convert 0.0°C to Kelvin, we apply the formula:
K = T(°C) + 273
Where T is the temperature in °C and K is the unknown temperature in Kelvin:
K = 0.0 + 273 = 273K
Problem 2
The combined gas law is also known as the general gas law. It is expressed as:
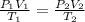
The expression combines both Boyle's law and Charle's Law.
Problem 3
Parameters given:
Volume of gas in the container V₁ = 22.4L
Pressure on the gas P₁ = 1.0atm
Temperature = 273K
P₂ = 1.50atm
Unknown: The final volume, V₂ = ?
Solution
From the given problem, we know that the temperature is constant. We apply Boyle's law. Boyle's law states that "The volume of a fixed mass of gas varies inversely a the pressure changes if the temperature is constant".
It is expressed as P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
The unknown parameter is V₂, we make it the subject of the expression:
V₂ =
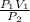
V₂ =
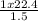
V₂ = 15L
Problem 4
The unknown here is the new volume V₂ at constant pressure.
Given parameters:
Volume of gas in the container V₁ = 22.4L
Pressure on the gas P is constant
Intial Temperature T₁ = 273K
Final Temperature T₂ = 100°C , converting to K gives, K = 100 + 273 = 373K
From the given parameters, the unknown and the conditions guiding the equation, we apply Charle's law. Charle's law states that "The volume of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature provided pressure is constant".
it is expressed as:
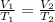
We then express the unknown V₂ as the subject of the formula:
V₂ =
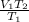
V₂ =
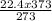
V₂ = 30.6L