3±√21. The equation
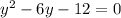 has two possible solutions 3+√21 y 3-√21.
has two possible solutions 3+√21 y 3-√21.
If we have a general quadratic equation
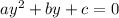 we can solves the equation by completing the square. First, we divide the quadratic equation by a, we obtain
we can solves the equation by completing the square. First, we divide the quadratic equation by a, we obtain
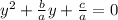 .
.
For this problem, we have
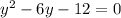
We can skipped division in this example since the coefficient of
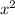 is 1.
is 1.
Move the term c to the right side of the equation
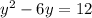
Completing the square on the left side of the equation and balance this by adding the same number to the right side of the equation, with b = -6.
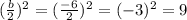
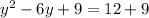
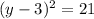
Take the square root on both sides of the equation:
y - 3 = ±√21
Add 3 from both sides:
y = 3 ± √21