Hello!
A 25.5 liter balloon holding 3.5 moles of carbon dioxide leaks. If we are able to determine that 1.9 moles of carbon dioxide escaped before the container could be sealed, what is the new volume of the container?
V1 (initial volume) = 25.5 L
n1 (initial number of moles) = 3.5 mol
V2 (final volume) = ? (in L )
Note: there was a leak in the number of moles, so we have:
n2 (final number of moles) = 3.5 mol - 1.9 mol = 1.6 mol
By Avogadro's Law it is known that the volume is directly proportional to the number of gas particles, that is, the larger the number of moles of gas, the greater its volume, on which we have the following relation:
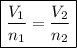
We apply the data to the formula, we have:
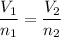
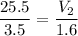
multiply the means by the extremes
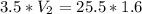
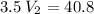


Answer:
The new volume of the container is approximately 11.66 liters
________________________