Answer: 1) Quadrant: I, reference angle:
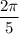
2) Quadrant: III, reference angle: 85°
3) Quadrant: IV, reference angle:
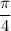
Explanation:
Reference angle is the angle closest to the x-axis
1) The given angle is (2/5)π. The first quadrantal (π/2) would be (2.5/5)π
Since (2/5)π < (2.5/5)π then it must be in Quadrant 1.
The angle closest to the x-axis is the same as the given angle.
2) The given angle is -95°. It is measured clockwise since it is a negative angle. Since it is greater than 90°, it is greater than the 270° quadrantal. So it must be in Quadrant III.
The angle closest to the x-axis is 85°.
3) The given angle is (23/4)π. Since (8/4)π is one rotation, this is greater than one rotation. (23/4)π - (8/4)π - (8/4)π = (7/4)π. So, it rotates two complete rotations and lands at coterminal angle (7/4)π.
The angle closest to the x-axis is π/4