Answer:
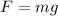
Step-by-step explanation:
Close to Earth's surface, the force of gravity that pulls an object towards the ground is
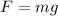 (2)
(2)
where
m is the mass of the object
g is the acceleration due to gravity, which is
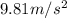 close to Earth's surface
close to Earth's surface
This is an approximation of the general formula of gravity valid only close to Earth's surface. The more general formula is
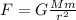 (1)
(1)
where
G is the gravitational constant
M is the Earth's mass
m is the object's mass
r is the distance of the object from Earth's center
At the Earth's surface,
r = R (Earth's radius), and by calling the following factor
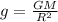
we see that eq.(1) becomes eq.(2).