4. A. Increase
The magnitude of the electric force between two charges is given by Coulomb's law:
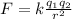
where
k is the Coulomb's constant
q_1 and q_2 are the two charges
r is the separation between the two charges
As we see from the formula, the strength of the electric force is:
- directly proportional to the two charges q1 and q2
- inversely proportional to the square of the distance r
Therefore, we can conclude that:
- if the magnitude of the charges increases, then the magnitude of the force will increases as well
- if the separation between the charges increases, then the magnitude of the force will decrease
5. A. Increase by the same factor
Again, the magnitude of the electric force between the two charges is given by Coulomb's law:
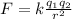
we have said that the force F is directly proportional to the two charges q_1 and q_2.
Let's assume now that charge q_1 is increases by a certain factor A. Then the electric force will change as follows:
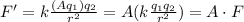
so, the magnitude of the electric force has increased by the same factor.
6. A. The electric force would decrease.
This part is similar to part 5, however this time the charge q_1 is decreased.
This means that we can rewrite the new charge q1 as
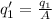
where A > 1. Let's see how the electric force changes:
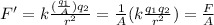
This means that the magnitude of the electric force has decreased by the same factor.