Answer:
- The first equation, a. PV = nRT, is not a valid statement of the ideal gas law.
Step-by-step explanation:
The basic expression for the ideal gas law is:
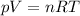 .......... [Equation 1]
.......... [Equation 1]
Where:
- n is the number of moles of the gas
- V is the volume occupied by the gas
- p is the pressure exerted by the gas molecules
- T is the temperature in absolute scale (Kelvin)
- R is the Universal gas constant (0.0821 atm-liter /K-mol or the equivalents in other units)
You can perform different algebraic operations to obtain equivalent equations:
Choice b) Divide equation 1 by T and you get:
- pV / T = nR, which is the choice b. from your list.
Choice c) Divide equation 1 by n × V and you get:
- p/n = RT / V, which is the choice c. from your list.
Choice d) Divide equation 1 n × T and you get:
- pV / (nT) = R, which is the choice d. from your list.
The choice a. p = nRTV states that p and V are in direct relation, when the ideal gas law states that p and V are inversely related, so that equation is wrong.
Conclusion: the choice a, p = nRTV, is not a statement of the ideal gas law.