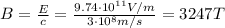1.
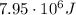
The total energy given to the cells during one pulse is given by:
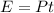
where
P is the average power of the pulse
t is the duration of the pulse
In this problem,
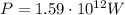
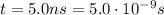
Substituting,
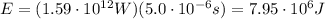
2.
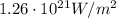
The energy found at point (1) is the energy delivered to 100 cells. The radius of each cell is
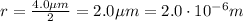
So the area of each cell is
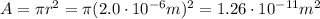
The energy is spread over 100 cells, so the total area of the cells is
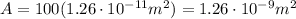
And so the intensity delivered is
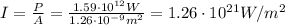
3.
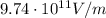
The average intensity of an electromagnetic wave is related to the maximum value of the electric field by
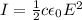
where
c is the speed of light
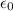 is the vacuum permittivity
is the vacuum permittivity
E is the amplitude of the electric field
Solving the formula for E, we find:

4. 3247 T
The magnetic field amplitude is related to the electric field amplitude by
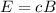
where
E is the electric field amplitude
c is the speed of light
B is the magnetic field
Solving the equation for B and substituting the value of E that we found at point 3, we find