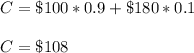Answer: Option D
D. $108
Explanation:
We must calculate the expected cost per patient to use treatment method B.
The expected cost for a discrete random variable x is:
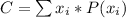
Where
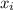 is the cost associated with the probability
is the cost associated with the probability
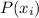
In this case, the random variable x is represented by the cost of each treatment.
For treatment B there is a possibility that antibiotic 2 works, in that case the cost x would be $ 100 and
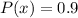
There is also the possibility that it does not work, in this case the cost x would be $180 and the probability
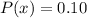
The expected cost is: