Answer:
see explanation
Explanation:
(5)
Using the trigonometric identity
sin²x + cos²x = 1 ⇒ cos²x = 1 - sin²x
Given
3sin²Θ + 2cos²Θ - 2
= 3sin²Θ + 2(1 - sin²Θ) - 2
= 3sin²Θ + 2 - 2sin²Θ - 2
= sin²Θ
(6)
Using the trigonometric identity
secx =
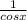
Consider the left side
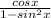
=
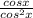
=
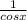 = secx = right side ⇒ verified
= secx = right side ⇒ verified
(7)
Using the trigonometric identity
1 + cot²x = csc²x
Given
sin²x. cot²x + sin²x ← factor out sin²x from each term
= sin²x(cot²x + 1)
= sin²x. csc²x
= sin²x ×
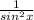 = 1
= 1