Answer: Option (b) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
A balanced equation is defined as the equation where number of atoms of the reactant equal to the number of atoms of the product.
This also means that mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of products in a chemical equation.
For example,
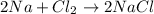
Total mass of reactants =
![[(2 * 23) + (35 * 2)] g/mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/a5ymxzu8uc0eprg2ynnbltl9zeg1heo47x.png)
= 116 g/mol
Total mass of products =
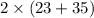 g/mol
g/mol
= 116 g/mol
Hence, mass if conserved in a chemical reaction.
thus, we can conclude that a balanced chemical equation shows the proportions of reactants and products necessary for mass to be conserved.