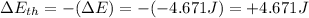1. 3.20 m/s
Assuming the string is inextensible, the cart and the weight travels the same distance: so, since the cart travels for 0.521 m, the distance travelled by the weigth is the same:
d = 0.521 m
The motion of the weigth is a free-fall motion with acceleration g = 9.8 m/s^2, so its final speed can be found by using the equation
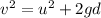
where
u = 0
is the initial speed of the weigth (at rest). Substituting into the formula, we find
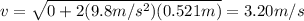
2. 1.022 J
The change in kinetic energy of the system is equal to the sum of the kinetic energies acquired by the cart and the weight. They both started from rest, so their initial kinetic energies were zero.
The cart has
mass: m = 1.000 kg
final speed: v = 0.931 m/s
so its gained kinetic energy is
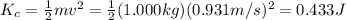
The weight has
mass: m = 0.115 kg
final speed: v = 3.20 m/s
so its gained kinetic energy is
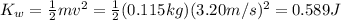
So the change in kinetic energy of the system is
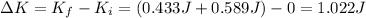
3. -5.693 J
The potential energy of the falling cart decreases by the following amount:
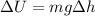
where
m = 1.000 kg is the mass
g = 9.8 m/s^2
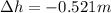 is the change in height of the cart
is the change in height of the cart
Substituting, we find
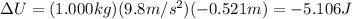
the potential energy of the falling weight decreases by the following amount:
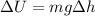
where
m = 0.115 kg is the mass
g = 9.8 m/s^2
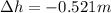 is the change in height of the weight (calculated at point a)
is the change in height of the weight (calculated at point a)
Substituting, we find
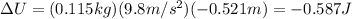
So, the change in potential energy is
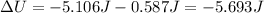
4. +4.671 J
The change in thermal energy of the system due to friction is equal to the loss in mechanical energy of the system.
The system has gained a kinetic energy equal to
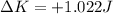
while it has lost a potential energy equal to
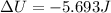
So the loss in mechanical energy of the system is
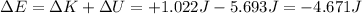
So the change in termal energy is