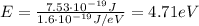Answer:
4.71 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
For an electromagnetic wave with wavelength
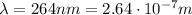
the energy of the photons in the wave is given by
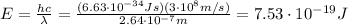
where h is the Planck constant and c the speed of light. Therefore, this is the minimum energy that a photon should have in order to extract a photoelectron from the copper surface.
The work function of a metal is the minimum energy required by the incident light in order to extract photoelectrons from the metal's surface. Therefore, the work function corresponds to the energy we found previously. By converting it into electronvolts, we find: