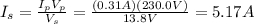1) 13.8 V
We can use the transformer equation:
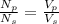
where we have
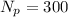 is the number of turns in the primary coil
is the number of turns in the primary coil
 is the number of turns in the secondary coil
is the number of turns in the secondary coil
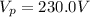 is the voltage in the primary coil
is the voltage in the primary coil
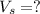 is the voltage in the secondary coil
is the voltage in the secondary coil
Solving for Vs, we find
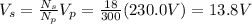
2) 5.17 A
For an ideal transformer, the power in input is equal to the power in output, so we can write:
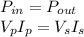
where
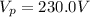 is the voltage in the primary coil
is the voltage in the primary coil
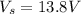 is the voltage in the secondary coil
is the voltage in the secondary coil
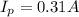 is the current in the primary coil
is the current in the primary coil
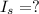 is the current in the secondary coil
is the current in the secondary coil
Solving for Is, we find