(a)
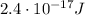
The De Broglie wavelength of a particle is given by
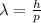 (1)
(1)
where
h is the Planck constant
p is the momentum of the particle
We also know that the kinetic energy of a particle (K) is related to the momentum by the formula
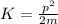
where m is the mass of the particle. Re-arranging this equation,
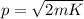 (2)
(2)
And substituting (2) into (1),
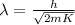 (3)
(3)
For an electron,
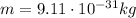
In the problem, the electron has a de broglie wavelength equal to the diameter of a hydrogen atom in the ground state:
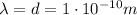
So re-arranging eq.(3) we can find the kinetic energy of the electron:
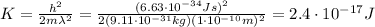
(b) Approximately 10 times larger
The ground state energy of the hydrogen atom is
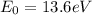
Converting into Joules,
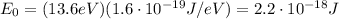
The kinetic energy of the electron in the previous part of the problem was
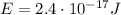
So, we see it is approximately 10 times larger.