Answer:
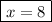
Explanation:
1. Jump discontinuity
In the graph, you can see that the left-hand limit of g(x) as x⟶ 8 is 3 and the right-hand limit is -3.
When the left- and right-hand limits at x = 8 exist but are different, we say that g(x) has a jump discontinuity at
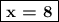 .
.
2. Other discontinuities
At x = 10, the left-hand limit is ∞ and the right-hand limit is -∞. Both one-sided limits are infinite, so this is an infinite discontinuity.
At x= 1, both one-sided limits are equal, but g(1) does not exist,
At x= 4, the limits are equal, and g(4) = 3.
In each case, the holes can be removed by redefining g(x), so the holes are removable discontinuities.