Answer:
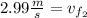
Step-by-step explanation:
We know that from collisions (be it elastic or inelastic), as long as there are no external forces acting on the system, the momentum stays the same, before the collision and after the collision, this is called the Law of Conservation of Momentum.
The formula for momentum is:
M=mass * velocity
So from the law of conservation of momentum, we have:
Initial Momentum (before the collision) = Final momentum (after the collision)
If you check the simple drawing, you get the meaning of the sign in front of the velocity.
Now, using the conservation of momentum law's formula we have:
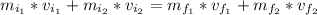
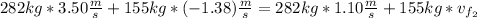
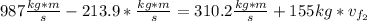
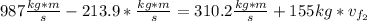
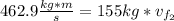
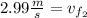 to the East
to the East