Final Answer:
The equation
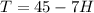 represents the relationship between temperature (T) and height above the surface (H) on the distant planet, where the surface temperature is 45 Celsius, decreasing by 7 Celsius for each kilometer of height. Graphing this equation reveals a linear line with a negative slope, portraying the systematic decrease in temperature as one moves higher above the planet's surface.
represents the relationship between temperature (T) and height above the surface (H) on the distant planet, where the surface temperature is 45 Celsius, decreasing by 7 Celsius for each kilometer of height. Graphing this equation reveals a linear line with a negative slope, portraying the systematic decrease in temperature as one moves higher above the planet's surface.
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation
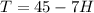 is derived from the given information about the distant planet's temperature. The surface temperature is 45 Celsius, and for each kilometer above the surface (represented by H), the temperature decreases by 7 Celsius.
is derived from the given information about the distant planet's temperature. The surface temperature is 45 Celsius, and for each kilometer above the surface (represented by H), the temperature decreases by 7 Celsius.
The equation reflects this linear relationship. The term 45 is the starting temperature at the surface, and the term -7H represents the decrease for each kilometer above.
For example, let's substitute H = 1 into the equation to find the temperature at a height of 1 kilometer:
![\[ T = 45 - 7(1) = 45 - 7 = 38 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/1t4jby1c28lt08yzpigrk3xy6qjupnnhyz.png)
This calculation shows that at a height of 1 kilometer, the temperature is 38 Celsius. Similarly, for H = 2:
![\[ T = 45 - 7(2) = 45 - 14 = 31 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/4ghhl4m3l8q0ry2xq655pb6nin3nlnktea.png)
This process can be repeated for different values of H to create a set of coordinates (H, T) that form a linear relationship. Graphing these points produces a straight line with a negative slope, illustrating the temperature decrease with increasing height.
In essence, the detailed calculation demonstrates how the equation captures the specified temperature-height relationship on the distant planet. It provides a mathematical representation of the observed data and allows scientists to predict temperatures at various heights above the surface.