Answer:
Because of the buoyant force
Step-by-step explanation:
Jumping into a pool change the amount of apparent gravity acting on a person.
Normally, for a person in free fall, the weight of the person is given by:
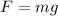
where m is the mass of the person and g=9.8 m/s^ is the acceleration due to gravity.
When a person is in the water, there is a buoyant force pushing the person upward. The magnitude of the buoyant force is
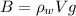
where
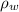 is the density of the water
is the density of the water
V is the volume of displaced fluid
g is the acceleration due to gravity
So the net force acting on the person is
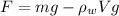 (1)
(1)
Since V corresponds to the volume of the person, we can rewrite it as
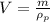
where
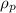 is the density of the person. Substituting into eq.(1),
is the density of the person. Substituting into eq.(1),
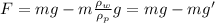 (2)
(2)
where we called
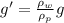
So we can further rewrite (2) as
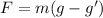
so we see that the gravity acting on the person, g, has been modified into (g-g') due to the presence of the buoyant force.