1. Helium nucleus and electron/positron
- An
 decay is a decay in which an
decay is a decay in which an
 particle is produced.
particle is produced.
An
 particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons: therefore, in an alpha-decay, the nucleus loses 2 units of atomic number (number of protons) and 2 units of mass number (sum of protons+neutrons).
particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons: therefore, in an alpha-decay, the nucleus loses 2 units of atomic number (number of protons) and 2 units of mass number (sum of protons+neutrons).
The alpha-particle consists of 2 protons of 2 neutrons: so it corresponds to a nucleus of helium, which consists exactly of 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
- There are two types of
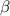 decay:
decay:
-- In the
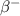 decay, a neutron decays into a proton emitting a fast-moving electron and an anti-neutrino:
decay, a neutron decays into a proton emitting a fast-moving electron and an anti-neutrino:
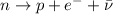
and the
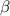 particle in this case is the electron
particle in this case is the electron
-- In the
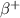 decay, a proton decays into a neutron, emitting a fast-moving positron and a neutrino:
decay, a proton decays into a neutron, emitting a fast-moving positron and a neutrino:
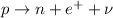
and the
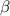 particle in this case is the positron.
particle in this case is the positron.
2) Gamma ray
A
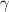 decay occurs when an unstable (excited state) nucleus decays into a more stable state. In this case, there are no changes in the structure of the nucleus, but energy is released in the form of a photon:
decay occurs when an unstable (excited state) nucleus decays into a more stable state. In this case, there are no changes in the structure of the nucleus, but energy is released in the form of a photon:
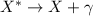
where the wavelength of this photon usually falls in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum corresponding to the gamma ray region.
So, the
 ray is commonly known as gamma radiation.
ray is commonly known as gamma radiation.
3)
The sign of the three forms of radiation are the following:
-
 particle: it consists of 2 protons (each of them carrying a positive charge of +e) and 2 neutrons (uncharged), so the total charge is
particle: it consists of 2 protons (each of them carrying a positive charge of +e) and 2 neutrons (uncharged), so the total charge is
Q = +e +e = +2e
-
 particle: in case of
particle: in case of
 radiation, the particle is an electron, so it carries a charge of
radiation, the particle is an electron, so it carries a charge of
Q = -e
in case of
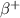 radiation, the particle is a positron, so it carries a charge of
radiation, the particle is a positron, so it carries a charge of
Q = +e
-
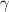 radiation: the
radiation: the
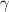 radiation consists of a photon, and the photon has no charge, so the charge in this case is
radiation consists of a photon, and the photon has no charge, so the charge in this case is
Q = 0