Answer:
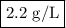
Step-by-step explanation:
We can use the Ideal Gas Law to calculate the density of the gas.
pV = nRT
n = m/M Substitute for n
pV = (m/M)RT Multiply both sides by M
pVM = mRT Divide both sides by V
pM = (m/V) RT
ρ = m/V Substitute for m/V
pM = ρRT Divide each side by RT
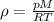
Data:
p = 1.00 bar
M = 49 g/mol
R = 0.083 14 bar·L·K⁻¹mol⁻¹
T = 0 °C = 273.15 K
Calculation:
ρ = (1.00 × 49)/(0.083 14 × 273.15) = 2.2 g/L
The density of the gas is
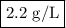 .
.