Answer:
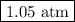
Step-by-step explanation:
We can use the Ideal Gas Law to calculate the pressure.
pV = nRT Divide both sides by V
p = (nRT)/V
p = (m/M)(RT/V) = (mRT)/(MV)
Data:
m = 100 g
R = 0.082 06 L·atm·K⁻¹mol⁻¹
T = 325 K
M = 253.81 g·mol⁻¹
V = 10 L
Calculations:
p = (100 × 0.082 06× 325)/(253.81 × 10) = 1.05 atm
The pressure in the container is
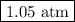 .
.