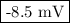Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The SHE is not under standard conditions, so we must use the Nernst Equation, which relates the cell potential to the standard potential and to the activities of the electroactive species.
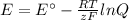
Step 1. Write the equation for the cell reaction
Anode: H₂(1 atm) ⇌ 2H⁺(1 mol·L⁻¹) + 2e⁻
Cathode: 2H⁺(0.88 mol·L⁻¹) + 2e⁻ ⇌ H₂(1.7 atm)
Overall: H₂(1 atm) + 2H⁺(0.88 mol·L⁻¹) ⇌ 2H⁺(1 mol·L⁻¹) + H₂(1.7 atm)
Step 2. Calculate Q
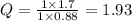
Step 3. Apply the Nernst equation
Data:
E° = 0 V
R = 8.314 J·K⁻¹mol⁻¹
T = 298 K
n = 2
F = 96 485 C/mol
Calculation:
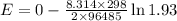
= -0.0128 × 0.658
= -0.0085 V
=