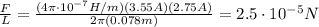Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The force per unit length between two current-carrying wires is given by:
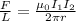
where
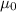 is the vacuum permeability
is the vacuum permeability
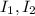 are the two currents
are the two currents
r is the separation between the wires
In this problem, we have
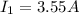 is the current in the first wire
is the current in the first wire
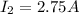 is the current in the second wire
is the current in the second wire
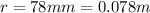 is the separation between the wires
is the separation between the wires
Substituting into the equation, we find