Answers:
A concave mirror, or convergent mirror, has a reflective surface that is curved inwards.
This type of mirrors reflect the light making it converge in a focal point therefore they are used to focus the light. This occurs because the light is reflected with different angles, since the normal to the surface varies from one point to another of the mirror.
Nevertheless, it is important to note the object must be within the radius of curvature of the lens or mirror.
In addition, it is important to state clear the following:
-If the object is at a distance greater than the focal distance, a real and inverted image is formed that may be greater or less than the object.
-If the object is at a distance smaller than the focal distance, a virtual upright image is formed that is larger than the object.
Having this clear, let’s begin with the answers:
a) Image distance when the object distance is 12.60 cm
The Mirror equation is:
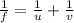 (1)
(1)
Where:
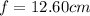 is the focal distance
is the focal distance
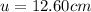 is the distance between the object and the mirror
is the distance between the object and the mirror
 is the distance between the image and the mirror
is the distance between the image and the mirror
Finding
 from (1):
from (1):
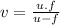 (2)
(2)
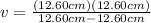
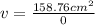 >>>>The division by zero is not defined!
>>>>The division by zero is not defined!
This is mathematically known as an indetermination, however, let's think a little bit:
If we divide something really big between something really small (tending to zero), the result will tend to infinite (
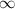 ).
).
This means:
When the object is placed just at the focal distance, the image is formed in the infinity, well in fact the image does not exist.
The answer is −1000cm
b) Image distance when the object distance is 6.30 cm
We will use the Mirror equation again:
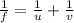 (1)
(1)
Where:
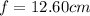 is the focal distance
is the focal distance
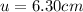 is the distance between the object and the mirror
is the distance between the object and the mirror
 is the distance between the image and the mirror
is the distance between the image and the mirror
Finding
 from (1):
from (1):
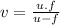 (2)
(2)
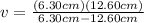
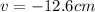 (3) >>>distance of the image
(3) >>>distance of the image
The negative sign indicates the distance between the image and the mirror is virtual
c) magnification of the image for part (b)
The magnification
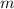 of the image is given by:
of the image is given by:
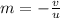 (4)
(4)
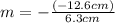
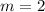 (5)
(5)
The fact that this value is positive means the image is upright
d) Description of the image
According to the explanations and results obtained in the prior answers, the correct option is 3:
The image is virtual, upright, larger than the object.