Answer:
d. Work is done on the gas
Step-by-step explanation:
We are considering an isobaric compression, which means:
- Isobaric: the pressure of the gas is constant
- Compression: the volume of the gas is decreasing
For an isobaric compression, the volume done BY the gas is
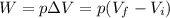
where
p is the gas pressure
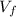 is the final volume of the gas
is the final volume of the gas
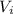 is the initial volume of the gas
is the initial volume of the gas
If the sign of W is positive, it means that the gas is doing work on the surrounding; if the sign of W is negative, it means that the surrounding is doing worn ON the gas.
In this case, since it is a compression, we have that the final volume is smaller than the initial volume:
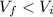
Therefore, the sign of W is negative, and therefore work is done ON the gas by the surroundings.