Answer: Option (d) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to rate law, rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of reactants.
For example,
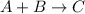
then, Rate = k [C]
Therefore, when we decrease the concentration of the reactant then there will also be decrease in the rate of a reaction.
Whereas when we increase the temperature then there is increase in rate of reaction due to increase in kinetic energy of molecules.
Thus, we can conclude that decreasing the concentration of the reactant will slow down a reaction.