Answer: A. 28.6 ml of the 0.7 M solution we need to start with.
B. There are 0.02 moles of solute were in the 0.7 M solution.
C. Amount of water to be added is 21.4 ml
D. The resulting solution will have concentration of 0.28 M
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the dilution law,
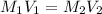
where,
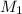 = molarity of stock solution = 0.7 M
= molarity of stock solution = 0.7 M
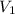 = volume of stock solution = ?
= volume of stock solution = ?
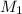 = molarity of diluted solution = 0.4 M
= molarity of diluted solution = 0.4 M
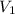 = volume of diluted solution = 50 ml
= volume of diluted solution = 50 ml
Putting in the values we get:
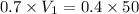
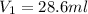
A. 28.6 ml of the 0.7 M solution we need to start with.
B. Molarity of a solution is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved per liter of the solution.
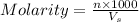
where,
n = moles of solute
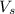 = volume of solution in ml
= volume of solution in ml
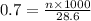
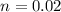
Thus there are 0.02 moles of solute were in the 0.7 M solution.
C. Amount of water to be added = (50-28.6 ) ml = 21.4 ml
D. If water added is
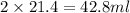
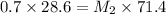
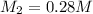
If volume of concentrated solution will be more , the resulting solution will have lesser concentration of 0.28 M