Answer:
The pressure of the chlorine gas with volume equal 5.90 L at 56°C is 1,473.7 Torr.
Step-by-step explanation:
The combined gas equation is,
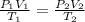
where,
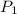 = initial pressure chlorine gas = 895 Torr =
= initial pressure chlorine gas = 895 Torr =
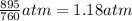
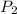 = final pressure chlorine gas = ?
= final pressure chlorine gas = ?
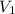 = initial volume chlorine gas =8.80 L
= initial volume chlorine gas =8.80 L
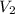 = final volume chlorine gas = 5.90 L
= final volume chlorine gas = 5.90 L
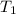 = initial temperature chlorine gas =
= initial temperature chlorine gas =
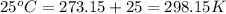
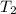 = final temperature chlorine gas =
= final temperature chlorine gas =
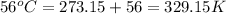
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get:
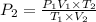
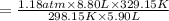
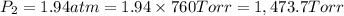
The pressure of the chlorine gas with volume equal 5.90 L at 56°C is 1,473.7 Torr.