Answer:
The De Broglie wavelength decreases when the momentum increases
Step-by-step explanation:
The De Broglie wavelength of a particle (or any object) is given by
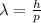
where
h is the Planck constant
p is the momentum of the object
As we can see, the wavelength is inversely proportional to the momentum of the object: therefore we can say that, if the momentum increases, the De Broglie wavelength will decrease.