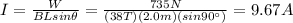Answer:
9.67 A
Step-by-step explanation:
The weight of a student with a mass of m = 75 kg is:
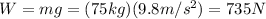
where g=9.8 m/s^2 is the acceleration due to gravity.
We want the magnetic force on the wire to be equal to this weight. The magnetic force on the wire is
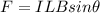
where
I is the current in the wire
L = 2.0 m is the length of the wire
B = 38 T is the magnetic field
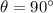 is the angle between the direction of B and L
is the angle between the direction of B and L
Since we want W=F, we can write
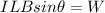
And we can solve it to find the current I: