If the moving object is undergoing constant acceleration, then
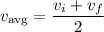
(take the average of the initial and final velocities, if they're given)
If you don't know the acceleration or initial/final velocities, then you have to resort to the usual definition,
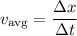
where
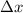 is the change in position and
is the change in position and
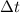 is the duration of the interval.
is the duration of the interval.