Answer:
KT = 60
OY = 11
Explanation:
Remember that the tangent to a circle theorem states that if a line is tangent to a circle, it is perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangency. Which means angles OTK and OYK are right angles.
If OTK and OYK are right angles, triangles KOT and KYO are right triangles. Since KOT is a right triangle, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find KT:
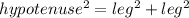
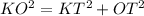
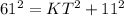
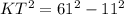
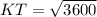
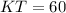
Now, remember that the "hat" theorem states that tangents to a circle from the same external point are congruent, so KT and KY are congruent.
The Hypotenuse-Leg theorem states that if the hypotenuse and a leg of one right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and a leg another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. The hypotenuse, KO, of both right triangles are the same (therefore congruent) and legs KT and KY are congruent by the hat theorem, therefore triangles KOT and KYO are congruent. Since corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent, OY ≅ OT.
OY = OT = 10
OY = 10
Let's summary the above in a short proof:
1. ∠OTK and ∠OYK are ∟ angles Tangent to a circle theorem
2. ΔOTK and ΔOYK are ∟ triangles Definition of right triangles
3. KT ≅ KY Hat theorem
4. KT = 60 Pythagorean theorem
5. OY ≅ OT CPCTC
6. OY = 10 Definition of congruency