(a) same direction as the electron's initial velocity
The direction of the acceleration is opposite to the direction of the velocity of the electron. This means that the electron is feeling a repulsive force, in a direction opposite to its initial velocity.
For a negative charge, we know that the electrostatic force and the electric field have opposite directions, because in the formula
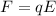
q is negative. Therefore, the electric field must be in the same direction as the initial velocity of the electron.
(b)
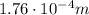
When the electron comes to rest, all its initial kinetic energy has been converted into electric potential energy. So we can write
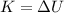
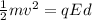
where
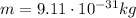 is the electron mass
is the electron mass
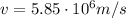 is the electron initial speed
is the electron initial speed
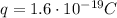 is the magnitude of the electron charge
is the magnitude of the electron charge
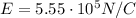 is the electric field
is the electric field
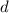 is the distance covered
is the distance covered
Solving the equation for d, we find
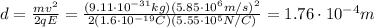
which corresponds to 0.17 mm.
(c)
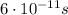
First of all, we need to find the electrostatic force acting on the electron:
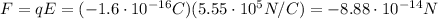
Now we can find the acceleration of the electron:
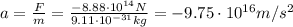
(the acceleration is negative because it is opposite to the electron's direction of motion)
And now we can find the time taken for the electron to stop to a velocity of v=0 starting from
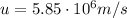 :
:
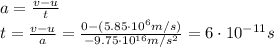
(d)
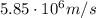
When it returns to the starting point, all the electric potential energy gained by the electron through the distance d will be re-converted back into kinetic energy. If there is no loss of energy, therefore, this means that the electron will have the same kinetic energy it had at the beginning of the motion: therefore, its speed will be equal to its initial speed,
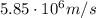 .
.