Answer:
C. increases
Step-by-step explanation:
The total resistance of a parallel circuit is given by:
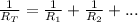
where R1, R2, etc. are the individual resistances.
From the formula, we notice that as new resistors are added to the configuration, the total resistance
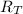 decreases.
decreases.
According to Ohm's law, the current flowing in the circuit is inversely proportional to the total resistance:
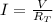
where V is the voltage supplied by the source: so, when adding more resistors in parallel, the total resistance decreases and the current increases.
Finally, the power supplied by the source is
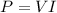
we said that V (voltage) remains constant, while I (the current) increases, so the power supplied increases as well.