Answer:
At constant pressure the new volume of gas is 12.878 L.
Step-by-step explanation:
Charles's Law consists of the relationship between the volume and temperature of a certain amount of ideal gas, which is maintained at a constant pressure, by means of a proportionality constant that is applied directly. So the ratio between volume and temperature will always have the same value:
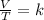
where the temperature is expressed in degrees kelvin (° K)
Then, when considering the two situations 1 and 2, keeping the amount of gas and the temperature constant, the relationship must be met:
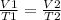
In this case, you know:
- V1= 10 L
- T1= 5 +273 = 278°K (where 0°C=273°K)
- V2= ?
- T2= 85 + 273 = 358°K
Replacing:
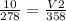
Solving:
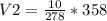
V2=12.878 L
At constant pressure the new volume of gas is 12.878 L.