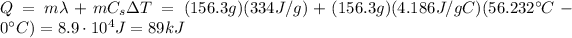1. 236 kJ
a. The phase (or state of matter) of the substance: from solid state to gas state (sublimation)
b. The enthalphy of sublimation, given by:
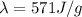
c. The equation to use will be
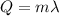 , where m is the mass of dry ice and
, where m is the mass of dry ice and
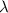 is the enthalpy of sublimation
is the enthalpy of sublimation
d. The energy is being absorbed, because the heat is transferred from the environment to the dry ice: as a consequence, the bonds between the molecules of dry ice break and then move faster and faster, and so the substance turns from solid into gas directly.
e. The amount of energy being transferred is
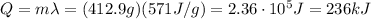
2. 165 kJ
a. The phase (or state of matter) of the substance: from gas state to liquid state (condensation)
b. The latent heat of vaporisation of water, given by
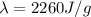
c. The equation to use will be
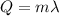 , where m is the mass of steam that condenses and
, where m is the mass of steam that condenses and
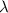 is the latent heat of vaporisation
is the latent heat of vaporisation
d. The energy is being released, since the substance turns from a gas state (where molecules move faster) into liquid state (where molecules move slower), so the internal energy of the substance has decreased, therefore heat has been released
e. The amount of energy being transferred is
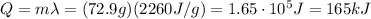
3. 3.64 kJ
a. Only the temperature of the substance (which is increasing)
b. The specific heat capacity of silver, which is
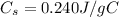
c. The equation to use will be
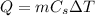 , where m is the mass of silver, Cs is the specific heat capacity and
, where m is the mass of silver, Cs is the specific heat capacity and
 the increase in temperature
the increase in temperature
d. The energy is being absorbed by the silver, since its temperature increases, this means that its molecules move faster so energy should be provided to the silver by the surroundings
e. The amount of energy being transferred is
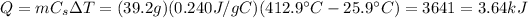
4. 89 kJ
a. Both the phase of the substance (from solid to liquid) and then the temperature
b. The latent heat of fusion of ice:
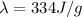 and the specific heat capacity of water:
and the specific heat capacity of water:
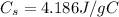
c. The equation to use will be
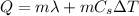 , where m is the mass of ice,
, where m is the mass of ice,
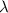 the latent heat of fusion of ice, Cs is the specific heat capacity of water and
the latent heat of fusion of ice, Cs is the specific heat capacity of water and
 the increase in temperature
the increase in temperature
d. The energy is being absorbed by the ice, at first to break the bonds between the molecules of ice and to cause the melting of ice, and then to increase the temperature of the water
e. The amount of energy being transferred is