(a)
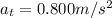
The tangential acceleration component of the car is simply equal to the change of the tangential speed divided by the time taken:
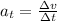
This rate of change is already given by the problem, 0.800 m/s^2, so the tangential acceleration of the car is
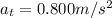
(b)
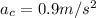
The centripetal acceleration component is given by
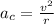
where
v is the tangential speed
r is the radius of the trajectory
When the speed is v = 3.00 m/s, the centripetal acceleration is (the radius is r = 10.0 m):
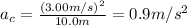
(c)
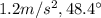
The centripetal acceleration and the tangential acceleration are perpendicular to each other, so the magnitude of the total acceleration can be found by using Pythagorean's theorem:
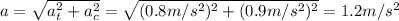
and the direction is given by:
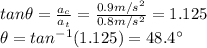
where the angle is measured with respect to the direction of the tangential acceleration.