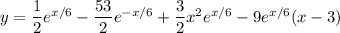The homogeneous ODE
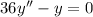
has characteristic equation
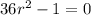
with roots at
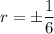 , and admits two linearly independent solutions,
, and admits two linearly independent solutions,
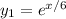
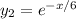
as the Wronskian is
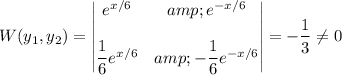
Variation of parameters has us looking for solutions of the form
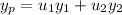
such that
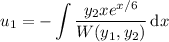
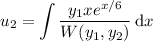
We have
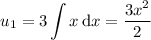
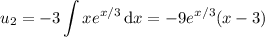
and we get
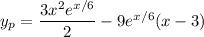
The general solution is
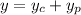
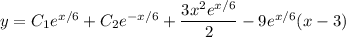
The initial conditions tell us
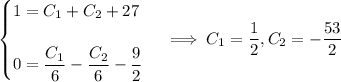
so that the particular solution is