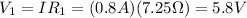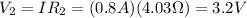a.
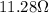
The equivalent resistance of a series combination of two resistors is equal to the sum of the individual resistances:
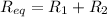
In this circuit, we have
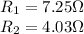
Therefore, the equivalent resistance is
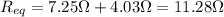
b. 5.8 V, 3.2 V
First of all, we need to determine the current flowing through each resistor, which is given by Ohm's law:
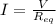
where V = 9.00 V and
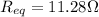 . Substituting,
. Substituting,
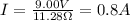
Now we can calculate the potential difference across each resistor by using Ohm's law again: