Step-by-step explanation:
According to Bronsted-Lowry, acids are the species that donate protons or
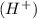 .
.
For example, HCl is a Bronsted-Lowry acid as it releases protons upon dissociation.
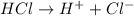
On the other hand, species that take up or accept a protons or
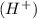 are known as Bronsted-Lowry base.
are known as Bronsted-Lowry base.
For example,
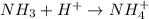
Therefore,
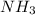 is a Bronsted-Lowry base as it accepts a proton.
is a Bronsted-Lowry base as it accepts a proton.