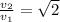1) D. The collisions between molecules are inelastic
Step-by-step explanation:
The kinetic theory of the gases describe the property of the gases by looking at microscopic level. At these level, some assumptions are made on the motion/collisions of the molecules of the gas:
- Molecules move by random motion
- The volume of the molecules is negligible compared with the volume of the gas
- The molecules obey Newton's laws of motion
- The intermolecular forces between the molecules are negligible except during the collisions
- Collisions between molecules are elastic
Therefore, the following statement
D. The collisions between molecules are inelastic
is wrong.
2)
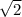
The kinetic energy Ek of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature T:
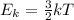
where k is the Boltzmann's constant. However, the kinetic energy depends on the square of the average velocity of the particles,
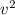 :
:
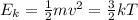
where m is the mass of the particles. This means that the velocity is proportional to the square root of the temperature:
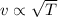
So, if the temperature of the gas is doubled, the average speed increases by a factor
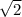 , and the ratio v2/v1 is
, and the ratio v2/v1 is