A formula known as law of cosine (sometimes also referred to as Carnot's rule) states that, in any triangle ABC, you have
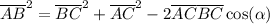
where
 is the angle between AC and BC. This formula generalizes Pythagoras' theorem, since it doesn't require the triangle to be right. In your case, we have
is the angle between AC and BC. This formula generalizes Pythagoras' theorem, since it doesn't require the triangle to be right. In your case, we have
![[tex]AB = \sqrt{(1)/(4)+(1)/(9)-2\cdot(1)/(2)\cdot(1)/(3)\cdot\cos(100)} = \sqrt{(13)/(36)-(\cos(100))/(3)} \approx 0.65](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ba8n8lvi7w5h149z5k0mioa7kmapkw5fdb.png)