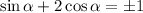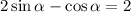
Consider the substitution
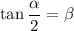 . Then by the double angle identities we get
. Then by the double angle identities we get
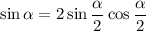
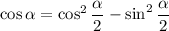
We also have
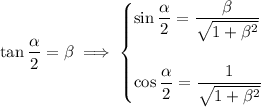
so that
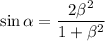
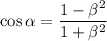
and the original equation has been transformed to
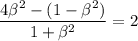
Solve for
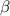 :
:
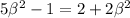
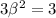
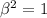
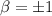
Solving for
 gives
gives
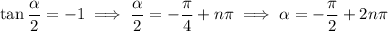
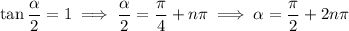
where
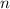 is any integer. Both
is any integer. Both
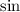 and
and
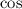 are
are
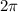 -periodic, which is to say
-periodic, which is to say
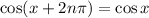
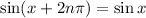
so that
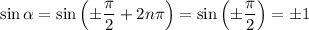
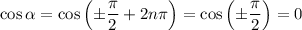
and we find that